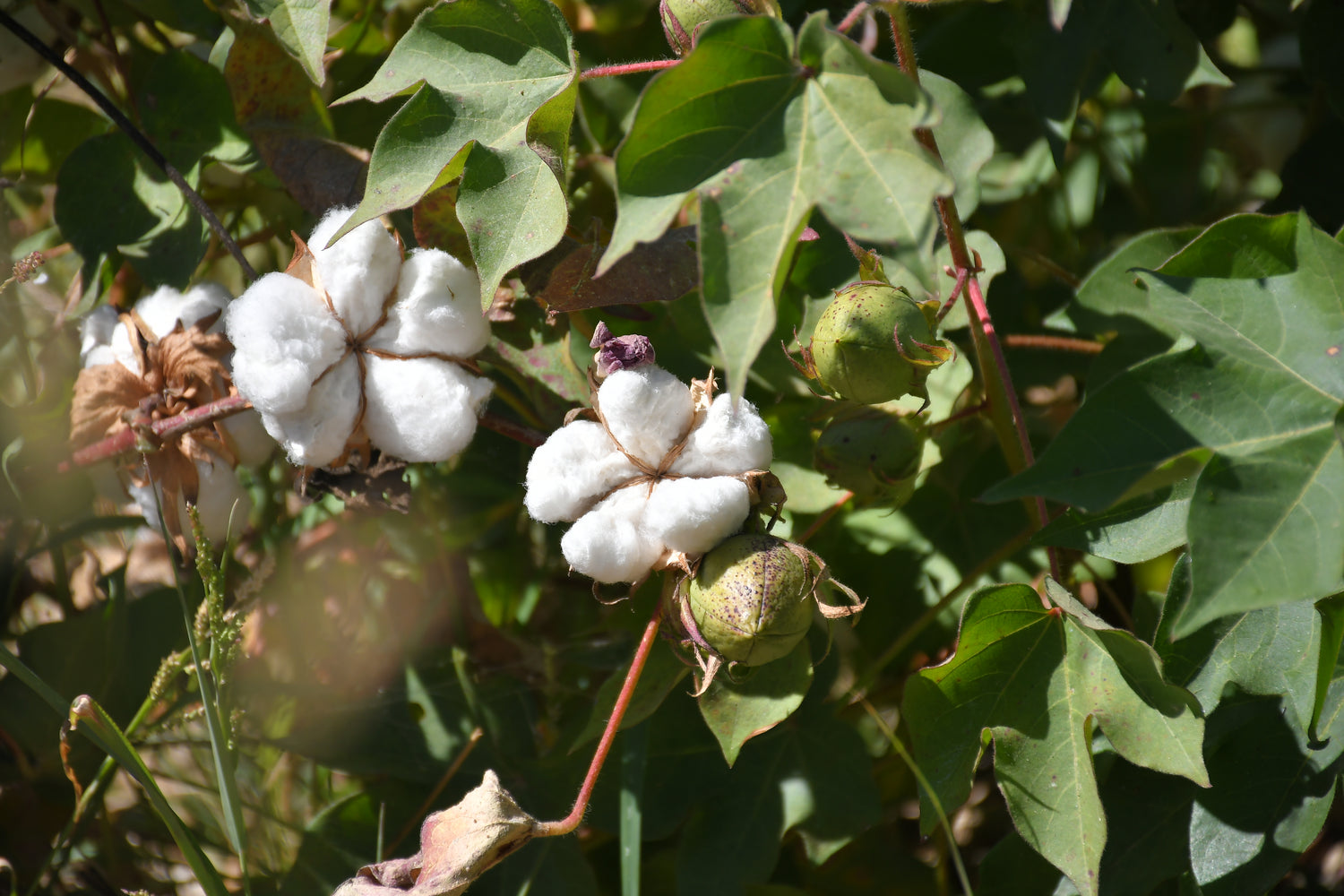
Regenerative Organic Cotton
In today's era of global warming, climate change, and escalating droughts, it has become increasingly evident that simply being sustainable is not enough to address the pressing environmental and social challenges we face. While sustainability focuses on minimizing negative impacts and preserving resources, it often falls short in actively restoring and regenerating the systems that sustain life. Holistic approach to sustainability that goes beyond mere preservation and aims to regenerating and healing, focusing on soli health and fertility. The destiny of soil, water and weather are all tied together.

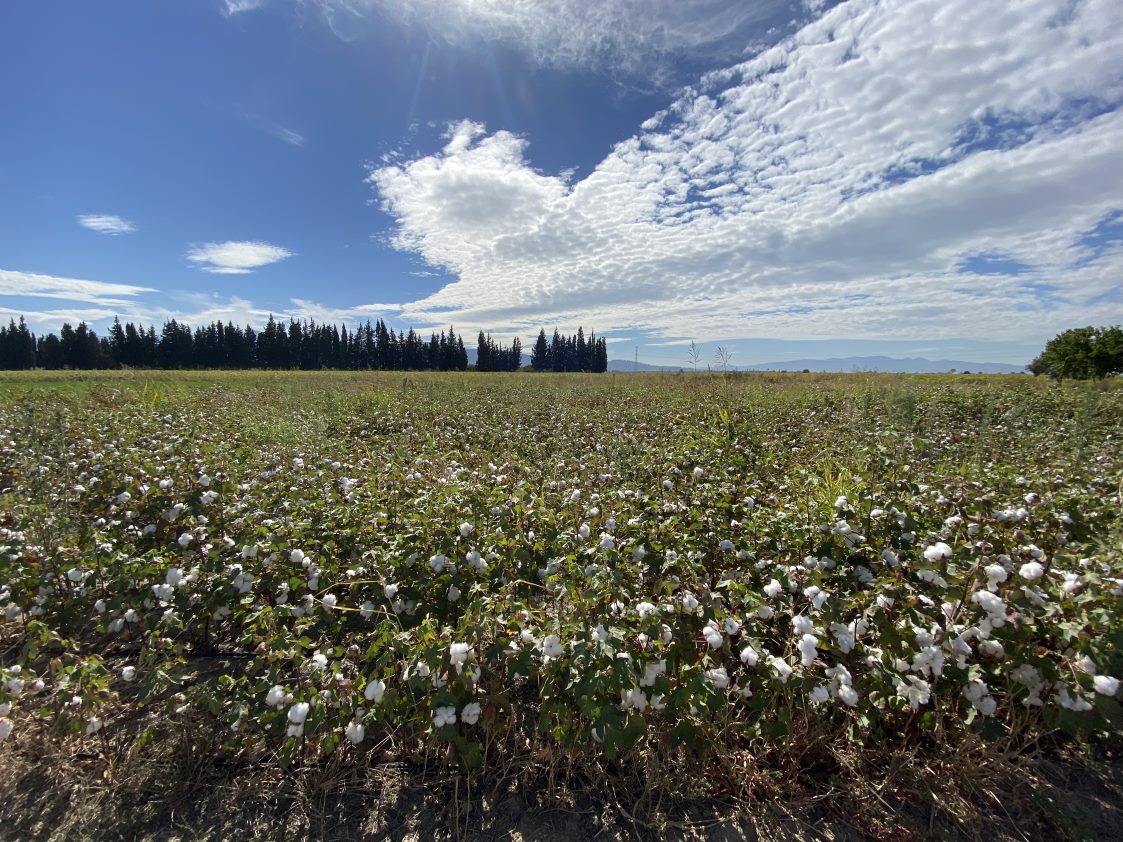
Why Regenerative Organic Cotton?
Regenerative organic cotton goes beyond organic farming principles by actively restoring and revitalizing the ecosystems it is grown in. This holistic approach prioritizes soil health, biodiversity, water conservation, and carbon sequestration. By nurturing the natural ecosystem, regenerative cotton aims to create a positive impact on the environment, communities, and the overall sustainability of the textile industry.

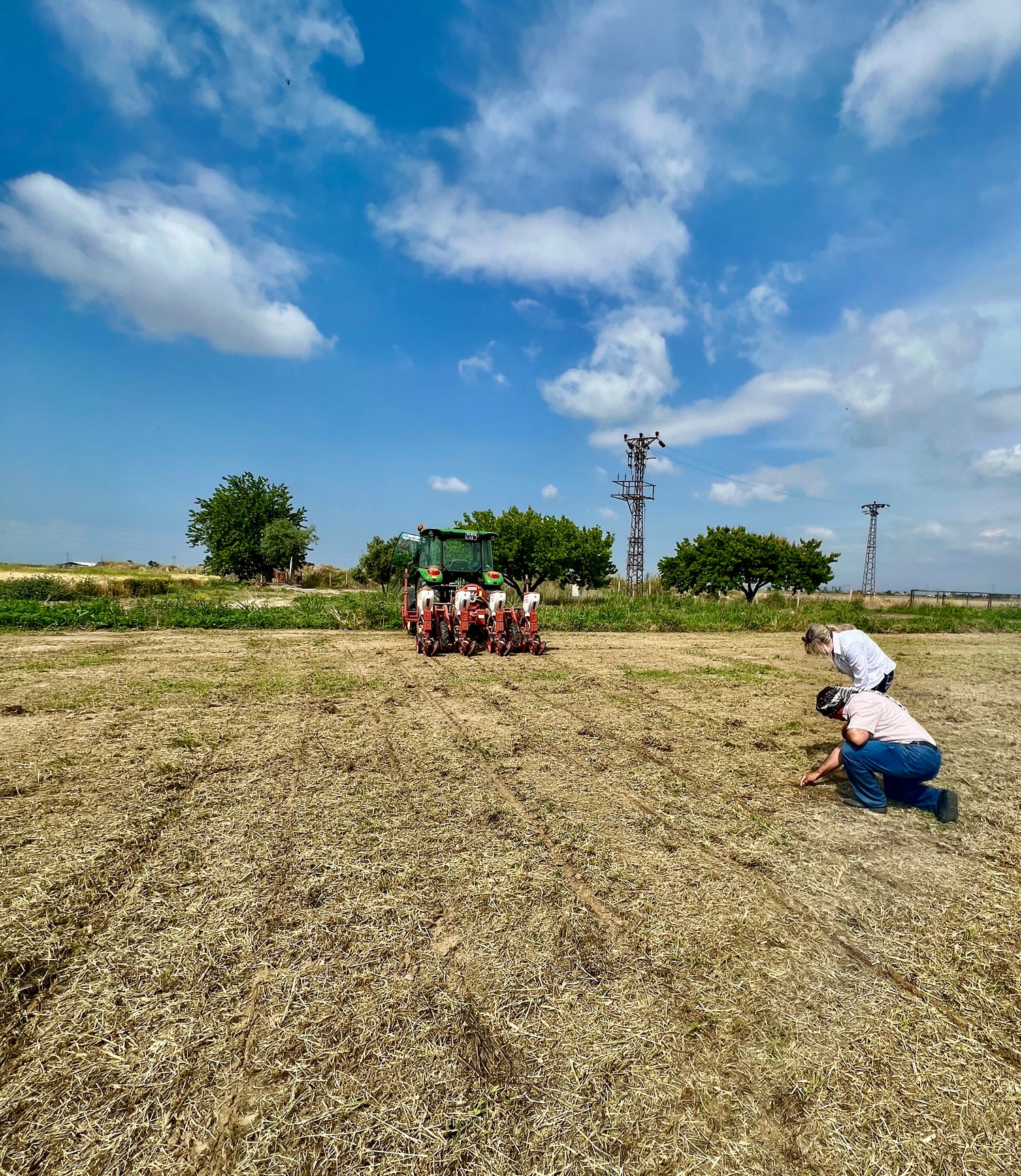
Our Regenerative Farms
As of 2021, we are running two projects for growing cotton by applying regenerative practices. Our regenerative organic cotton field located in Menemen, Izmir, is by cooperation of Ecological Agriculture Association (ETO) and International Agricultural Research and Training (UTAEM), where we constantly tracking soil health and organic content of soil. The other project is by cooperation of private sector and growing regenerative organic cotton and Turkish hemp side by side, located in Mendres, Izmir. We keep the distances from our operational office as short as possible to lessen our transpirational carbon footprint.
Our Regenerative Practices

No tilling
- We avoid tilling the soil, as it disrupts the natural structure and microbial activity. This practice helps to preserve soil health, minimize erosion, and retain organic matter.
Mulching
- We utilize mulching as a regenerative practice to improve soil quality and fertility. Mulch, made from plant residues, covers the bare land area, protecting the topsoil from erosion caused by wind and rain. Over time, the mulch decomposes, releasing organic nutrients that benefit the cotton crops and enrich the soil.
Cover Crops
- By planting cover crops such as oats, barley, and triticale, we increase biodiversity and provide natural ground cover during the off-season. These cover crops help prevent soil erosion, improve soil fertility, and enhance water retention.
Crops Rotation
- We practice crop rotation, which involves alternating different crops in the same field over different seasons. This technique helps replenish soil nutrients and prevents the depletion of specific nutrients, resulting in healthier soil and improved crop yields.
CO2 Emissions Measurements
The Carbon Flux Tool employs a method known as chamber settling in specific parts of the soil, where measurements are taken on a monthly basis. This technique helps us monitor the carbon dioxide levels and fluxes within the soil, providing valuable insights into the carbon sequestration process. Additionally, we also collect plant samples to calculate the total CO2 emissions, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of our carbon impact.The integration of the Carbon Flux Tool with mobile devices allows us to access and visualize the data conveniently. By having instant access to the measurements, we can track the progress of carbon sequestration efforts, identify areas for improvement, and optimize our regenerative practices accordingly.
Regenerative Agriculture Practices Focus On:
-
Soil Health
Soil health is foundational to regenerative farming. Unlike conventional or organic farming which may deplete the soil, regenerative practices aim to enhance and restore soil quality. Soil health and micro organism in soil matters.
-

Carbon Sequestration
Carbon sequestration is the process of capturing atmospheric carbon dioxide and storing it in the soil. Regenerative farming practices can enhance this natural process, turning farms into carbon sinks, which can help combat climate change.
-
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variety of life found in a particular ecosystem. In regenerative farming, fostering biodiversity is crucial. A diverse farm ecosystem is more resilient, can better resist pests, and supports a balance of predator-prey relationships.